Explain the Differences Between the Layers of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Explain the structure and function of. They are all discharged through tubular ducts.
From The Lumen Outward What Are The Layers Of The Gastrointestinal Tract Socratic
Bacterial Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract.

. Exocrine glands release their contents through a duct that leads to the epithelial surface. Explain the difference between a positive stain and a negative stain. After exposure and adhesion the next step in pathogenesis is invasion which can involve enzymes and toxinsMany pathogens achieve invasion by entering the bloodstream an effective means of dissemination because blood vessels pass close to every cell in the body.
Secretions into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract technically outside of the body are of the exocrine category. Know the histological differences in the pharynx and the upper middle and lower portions of the esophagus. List two physiologic factors that can alter each of the processes of absorption distribution and excretion.
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is characterized by repetitive episodes of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract caused by an abnormal immune response to gut microflora. Compare the roles of passive diffusion and carrier-medi-. Explain how bioavailability can impact drug response and product selection.
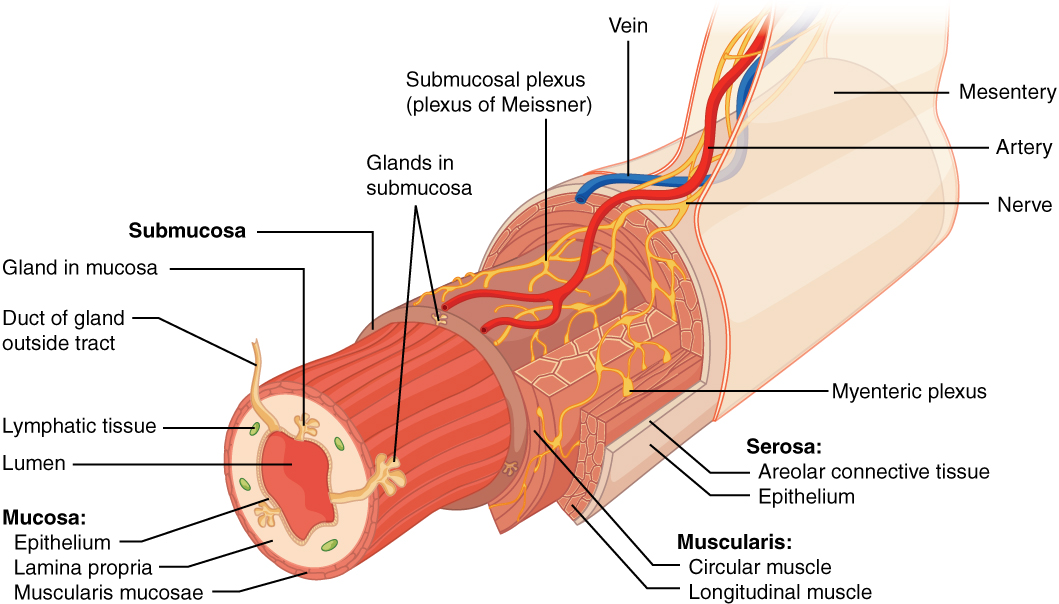
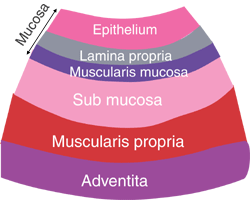
This course can be found in. Be able to describe the layers in the wall of the digestive tract mucosa submucosa muscularis propria and adventitiaserosa and explain how they differ in the pharynx esophagus and stomach. Secretions into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract technically outside of.
Mucous sweat saliva and breast milk are all examples of secretions from exocrine glands. Inflammatory bowel disease encompasses two types of idiopathic intestinal disease that are differentiated by their location and depth of involvement in the bowel wall. Viral Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract.
Bacterial Exoenzymes and Toxins as Virulence Factors. Making the crystal violetiodine complex clump and stay contained in thick layers of. Explain the meaning of the terms absorption distribu-tion metabolism and excretion.
Non è possibile visualizzare una descrizione perché il sito non lo consente. Be able to describe the layers in the wall of the digestive tract mucosa submucosa muscularis propria and adventitiaserosa and explain how they differ in the pharynx esophagus and stomach. TEAS Test Prep Thousands of practice questions an in-depth TEAS study guide and 200 test prep video lessons.
When food enters the mouth and passes through the digestive system it sends a multitude of interacting signals to the brain loaded with sensory nutritive and other information. The resting physical properties of these layers such as stiffness resting tension and Poisson ratio vary along the length of the gastrointestinal tract 11121314 Box 1. In the first session of the workshop moderated by Danielle Greenberg11Daniel Greenberg PhD FACN is a Food Forum member and was a member of the workshop planning committee.
They are all discharged through tubular ducts. Know the histological differences in the pharynx and the upper middle and lower portions of the esophagus. The epithelial cells exhibit polarity with differences in structure and function between the exposed or apical facing surface of the cell and the basal surface close.

Difference Between Muscularis Layer Of Esophagus And Stomach Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Comments
Post a Comment